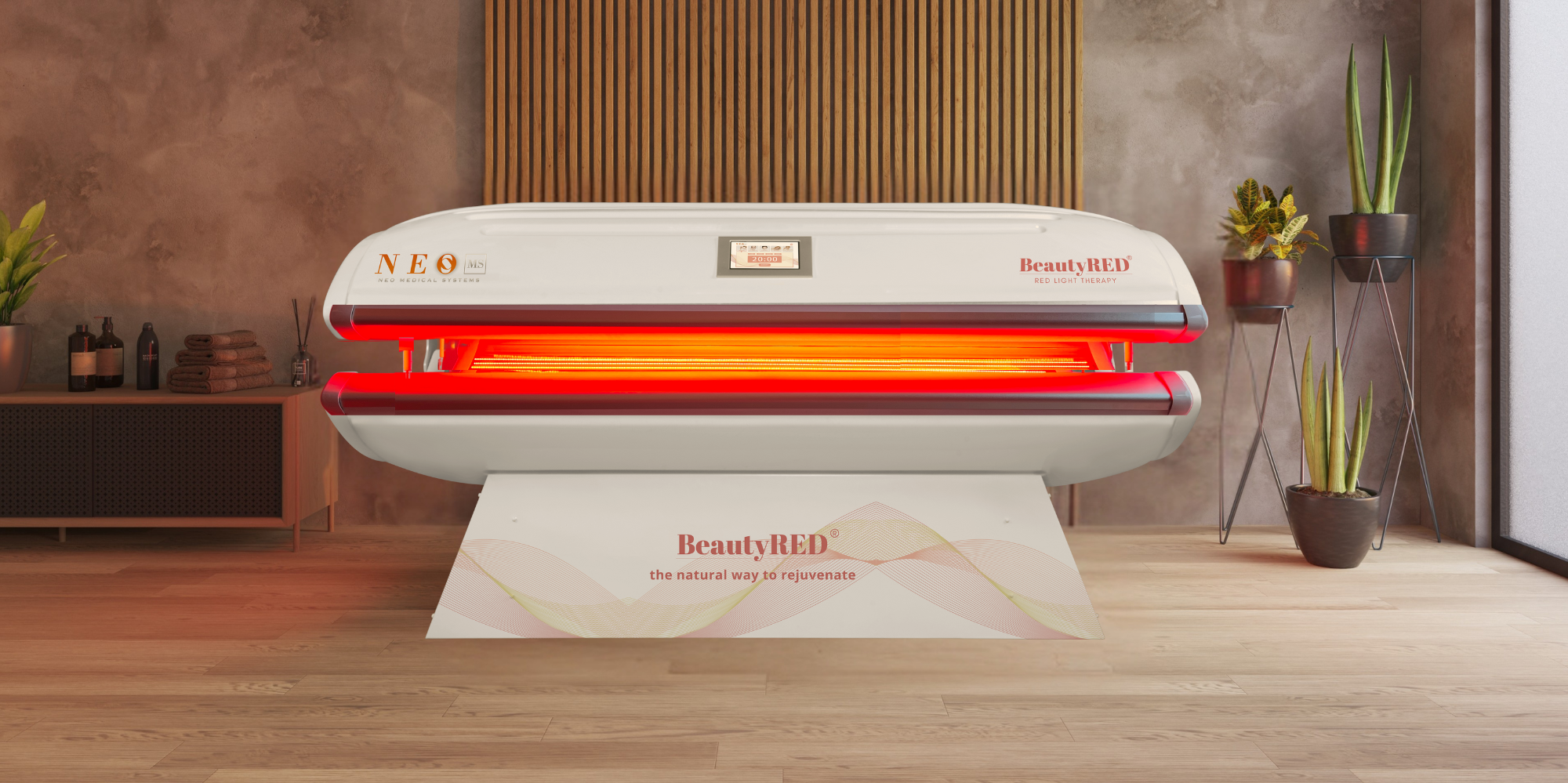
Find out more about the science behind light therapy.
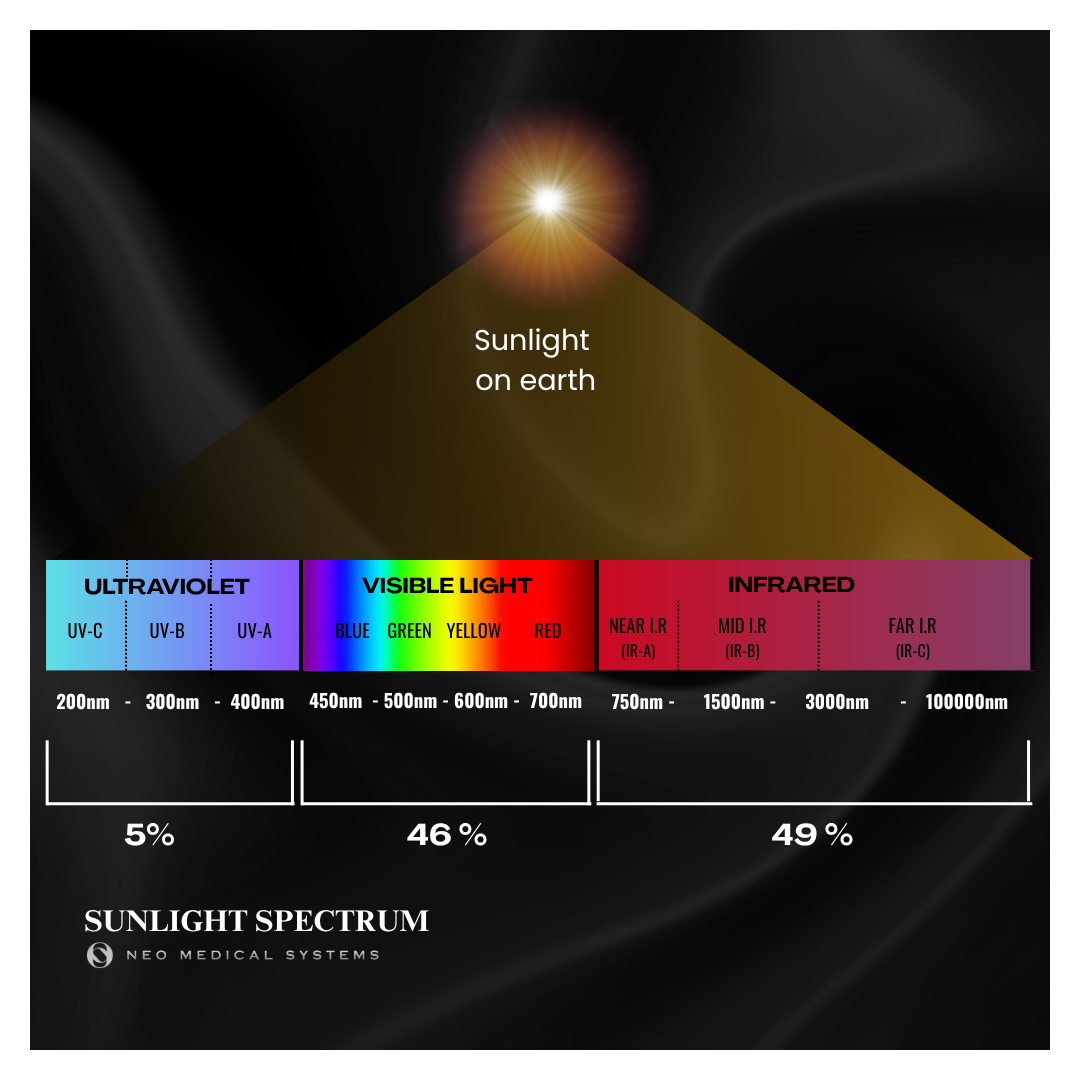
Solar radiation.
The most abundant energy source on Earth, solar energy drives the water cycle, wind, and photosynthesis, which in turn is the source of fossil fuels. All life on Earth depends on this energy source.
Solar radiation is an emission of particles. This stream of particles, called photons, reaches the Earth with different wavelengths, each corresponding to a specific energy. The energy distribution of the different wavelengths of the Sun's electromagnetic radiation is called the solar spectrum.
Visible light accounts for 46% of the total energy emitted by the sun.
49% of the energy radiation emitted by the sun is beyond the visible red spectrum, in the infrared range. It is this radiation that we feel as a heat wave.
The rest of solar radiation, ultraviolet radiation, represents all radiation with wavelengths shorter than those at the violet end of the visible spectrum.
VISIBLE LIGHT SPECTRUM.
Visible light accounts for 46% of the total energy emitted by the sun.
The visible light spectrum is the segment of the electromagnetic spectrum that humans can see, ranging from approximately 380 to 700 nanometers. It includes the colors of the rainbow—violet, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red—with violet having the shortest wavelength and red having the longest. When combined, these colors appear as white light, like sunlight.
Blue and violet light: these have shorter wavelengths (between 380 and 500 nm) and higher energy, so they cannot penetrate deeper than the dermis. (top layer of the skin). Primary biological impact: Regulates circadian rhythm, alertness, mood; antimicrobial effects; may cause oxidative stress in excess.
Green, yellow, and red light: these have longer wavelengths (between 550 and 700 nm) and lower energy, allowing them to penetrate deeper into the skin to reach the hypodermis (fat layer)
Green light (500-570 nm) : Calming effect, reduces migraine sensitivity, may aid pain modulation;
Yellow light (570 - 590 nm): Mild mood-enhancing and energizing; limited direct biological data;
Orange/Red light (590 - 700 nm): Stimulates cellular metabolism, increases ATP production, improves circulation, reduces inflammation;
INFRARED RANGE.
Infrared light accounts for 49% of the total energy emitted by the sun. Infrared (IR) light is invisible to the human eye but felt as heat. It lies just beyond red light on the electromagnetic spectrum, with wavelengths from about 700 nanometers (nm) to 1 millimeter (mm).
Infrared is divided into three main types:
Near-infrared Light (IR-A): with wavelength between 760 nm and 1400 nm, near-infrared light can penetrate skin slightly.
Mid-infrared Light (IR-B): with wavelength between 1400 nm to 3000 nm, Mid-infrared light can penetrate much deeper into the dermis, reaching the hypodermis (fat layer).
Far-infrared Light (IR-C): with wavelength between 3000 nm to 1,000,00 nm (1mm), far-infrared light carries most of the heat energy we feel from sunlight or heaters. “Low in frequency and therefore low in energy, far-infrared light is strongly absorbed by water in the outer layers of the skin, where it is converted to heat. This surface warmth gradually spreads inward through the tissues.
ULTRAVIOLET
Ultraviolet (U.V) accounts for 5% only of the total energy emitted by the sun. Ultraviolet are invisible to the human eye and the lens of the human eye acts as a natural filter, blocking most UV light before it can reach the light-sensitive retina. This filtering is an evolutionary adaptation to protect the eye from the high energy of UV light, which can cause damage.
Ultraviolet light is divided into three main regions:
U.V-A, with a wavelength between 315−400 nm (nanometers), they have the lowest energy of the three bands so they can penetrate deeper in the skin to reach the dermis. U.V-A ccounts for approximately 95% of the UV radiation that reaches the Earth's surface. Main biological effects: causes premature skin aging (wrinkles, sun spots) and contributes to skin cancer.
U.V-B: with a shorter wavelength between 280-315 nm, their medium-range energy penetrates less deeper into the body to reach the epidermis (top-layer of the skin). U.V-B accounts for the remaining 5% of UV radiation from the sun. Main biological effects : Primary cause of sunburn, skin cancer, and DNA damage.
U.V-C: with a much shorter wavelength between 100-280 nm, and the highest energy, they can’t even reach the Earth's surface from the sun. UV-C are very harmful for the human skin. UV-C is well-known for its germicidal effect, which inactivates microorganisms like bacteria and viruses by damaging their DNA or RNA. This property makes UVC widely used for disinfection in various settings, from sterilizing medical equipment to purifying water and air.
Where does red light therapy come from?
In 1993, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) began experimenting with red light therapy for plant growth in space and then to help heal wounds in astronauts. Later in October 1995, sources of red light—part of the visible spectrum of light—made their space shuttle flight debut on the second U.S. Microgravity Laboratory Spacelab mission (STS-73, Columbia) as part of experiments in plant growth.
Nowadays red light therapy is already widely medically accepted in its use in photodynamic therapy.
Now, RLT is being investigated (or already in use) for treating a wide array of health conditions. What’s confusing — and controversial — is the effectiveness of the treatment for the purposes it’s being promoted.
sources: Forbes & Cleveland Clinic
Decrease sign of aging & Collagen
The skin is largely made of collagen, a protein that prevents it from sagging and keeps it looking and feeling plump. While collagen is naturally produced by the body, sun exposure, smoking, pollution exposure and aging decrease production causing skin to lose elasticity and appear to sag and wrinkle. A 2014 study found full-body exposure to red light over the course of 30, twice-a-week sessions increased collagen density on participants’ faces and caused visible improvements in wrinkles and skin roughness.
How effective is RLT for wound healing?
As research in the journal AIMS Biophysics notes, many of the conditions that RLT treats have their roots in inflammation. Although the exact reason is not yet clear, RLT has significant anti-inflammatory effects and increase fibroblast production, which makes collagen.
What factors improve RLT?
Irradiance = amount of energy a specific part of your body receives over a set period. A higher irradiance can result in better results for less time. The most used format to measure irradiance is mW/cm2 (milliwatts per square centimetres). However, just stating the irradiance measurement means nothing if the distance is not provided. Some RLT devices have a high mW/cm2 reading on the surface of the device, and not on the object exposed to it.
Frequency: The range of frequency used in typical RLT devices is from 610 nm (a deep red, penerates the skin and acts on mitochondria) to 950 nm (near-infrared, penetrates deeper into tissue)
Treatment coverage area: it’s alway a better idea to use a RLT device with the maximum coverage as larger devices emit more light energy and better performance than smaller units like at-home devices.
RLT vs laser vs pulsed light?
RLT is different from laser or intense pulsed light (IPL) therapies because it doesn’t cause damage to the skin surface. Laser and pulsed light therapies work by causing controlled damage to the outer layer of the skin, which then induces tissue repair. RLT bypasses this harsh step by directly stimulating regeneration of the skin. The red light is natural and can penetrate deep into the skin, where the cells can absorb and use it.